

Find Your Industrial Maintenance Test Practice- IST, Ramsay, and More
Mechanics and Technicians are often required to take an Industrial Skills Test, or other industrial maintenance tests, to pass the first stage of the hiring process.
Each type of assessment poses different challenges, so to prepare for it you should first find the relevant test for you.
Below you can find the relevant test and practice for you, with a complete guide specifying employers and positions that typically require taking the test, along with free sample questions for common tests.
Looking for a different test? please feel free to contact us and we will guide you to the most accurate practice tests for your assessment.

ask_the_team@jobtestprep.com
The Industrial Skills test (IST) is an assessment used to determine the level of reading comprehension, numerical reasoning, and mechanical aptitude of prospective employees for a range of mechanically oriented occupations.
The IST test is widely used by PGE and other companies to select candidates for various positions:
The Industrial skills test can be used for entry-level positions, as well as for level 3 technicians.
After rising very slowly for millennia, the number of humans on Earth was just starting to take off. A century and a half later, when another scientist reported the discovery of human egg cells, the world’s population had doubled to more than a billion. A century after that, around 1930, it had doubled again to two billion. The acceleration since then has been astounding.
Two billion Half a billion One billion A quarter of a million View ExplanationThe correct answer is (C).
According to the passage: "A century after that, around 1930, it had doubled again to two billion." So a century before, in 1830, the number of people on Earth was half of that – one billion.
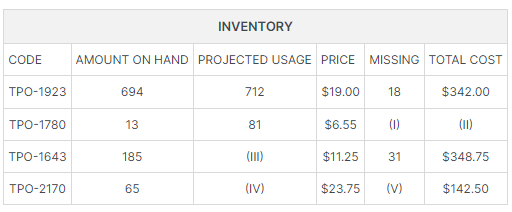
What is the value of (I)?
View ExplanationThe correct answer is B.
The first step in filling in missing values is to analyze the descriptions of the information given and figure out the relationships between them.
The CODE is a way to identify the type of inventory.
AMOUNT ON HAND refers to the number of units in the warehouse.
PROJECTED USAGE refers to number of units the company expects to use over the next period.
The PRICE tells us how much each unit costs.
MISSING likely refers to difference between the number of units in the warehouse and the number of units the company expects to use. If this is true, we would be able to formulate the equation:
(1) PROJECTED USE – AMOUNT ON HAND = MISSING
We can now take a row with these given values to check that this equation is in fact correct.
We will use Row 1 (TPO-1923), as it is the only row with all of these values given.
712 – 694 = 18, which is in fact the value given to MISSING.
TOTAL COST may refer to the total cost of the inventory on hand, the total cost of the projected usage or the total cost of the missing inventory. If we divide the TOTAL COST of TPO-1923 by the PRICE, we will see that 342 ÷ 19 = 18 which represents the MISSING value. We can therefore conclude that:
(2) PRICE × MISSING = TOTAL COST
Now that we have identified the correct equations, we simply need to place the correct numbers into the equations to find the missing values.
(I) is the MISSING value for item TPO-1780.
If we place the values given into equation (1) we will get: 81 – 13 = 68.